How does a Vice tablet press work?
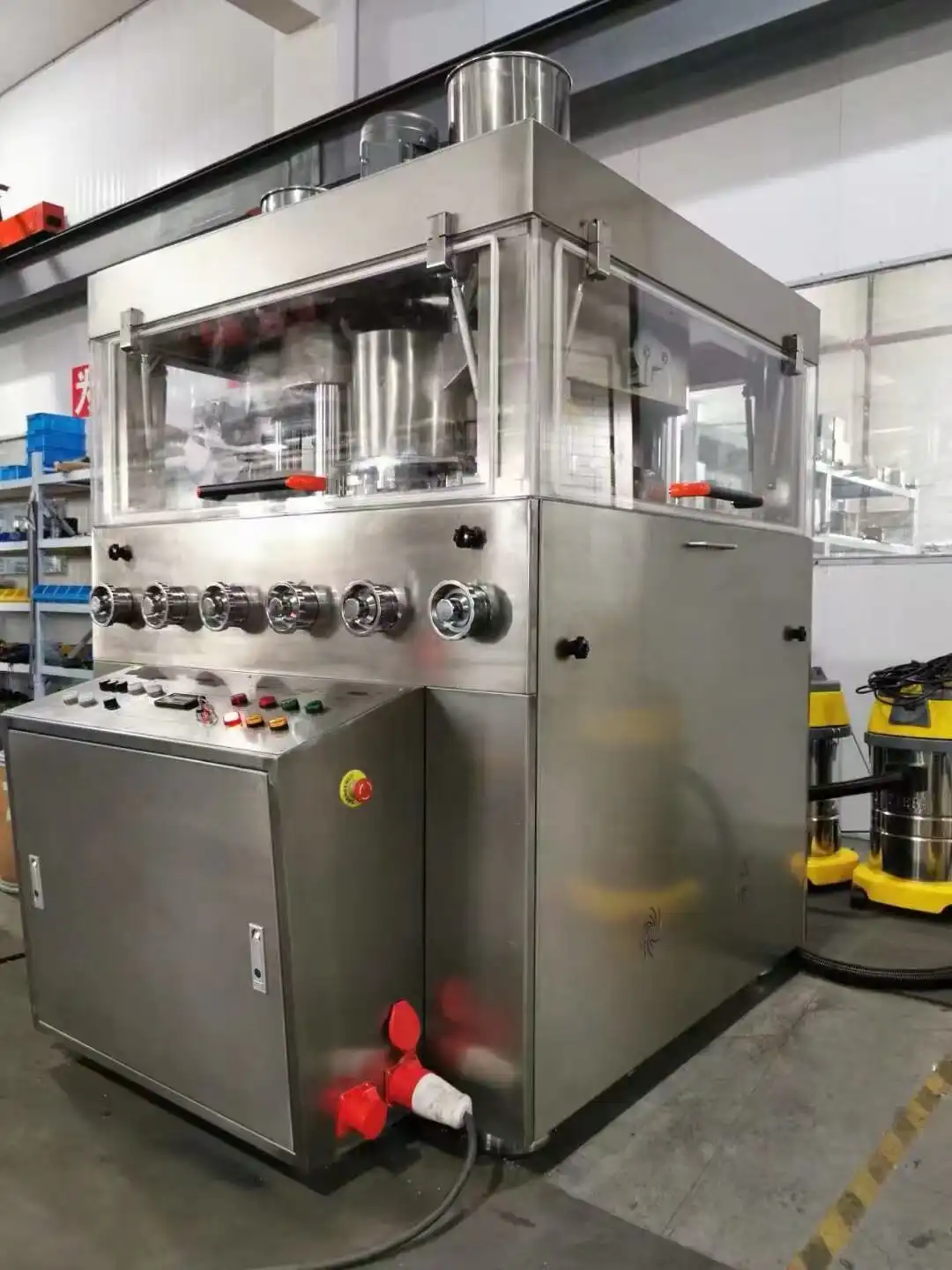
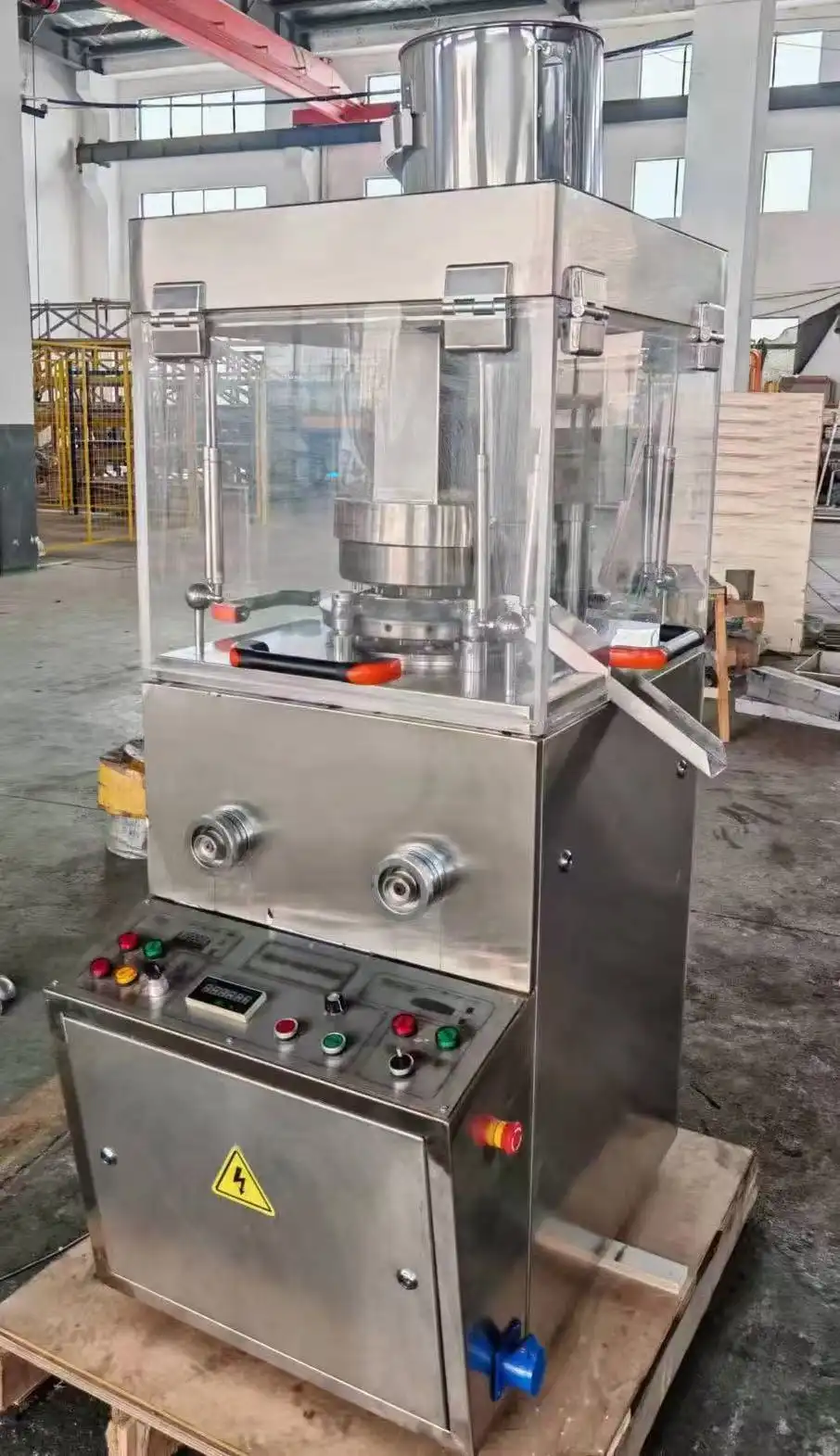
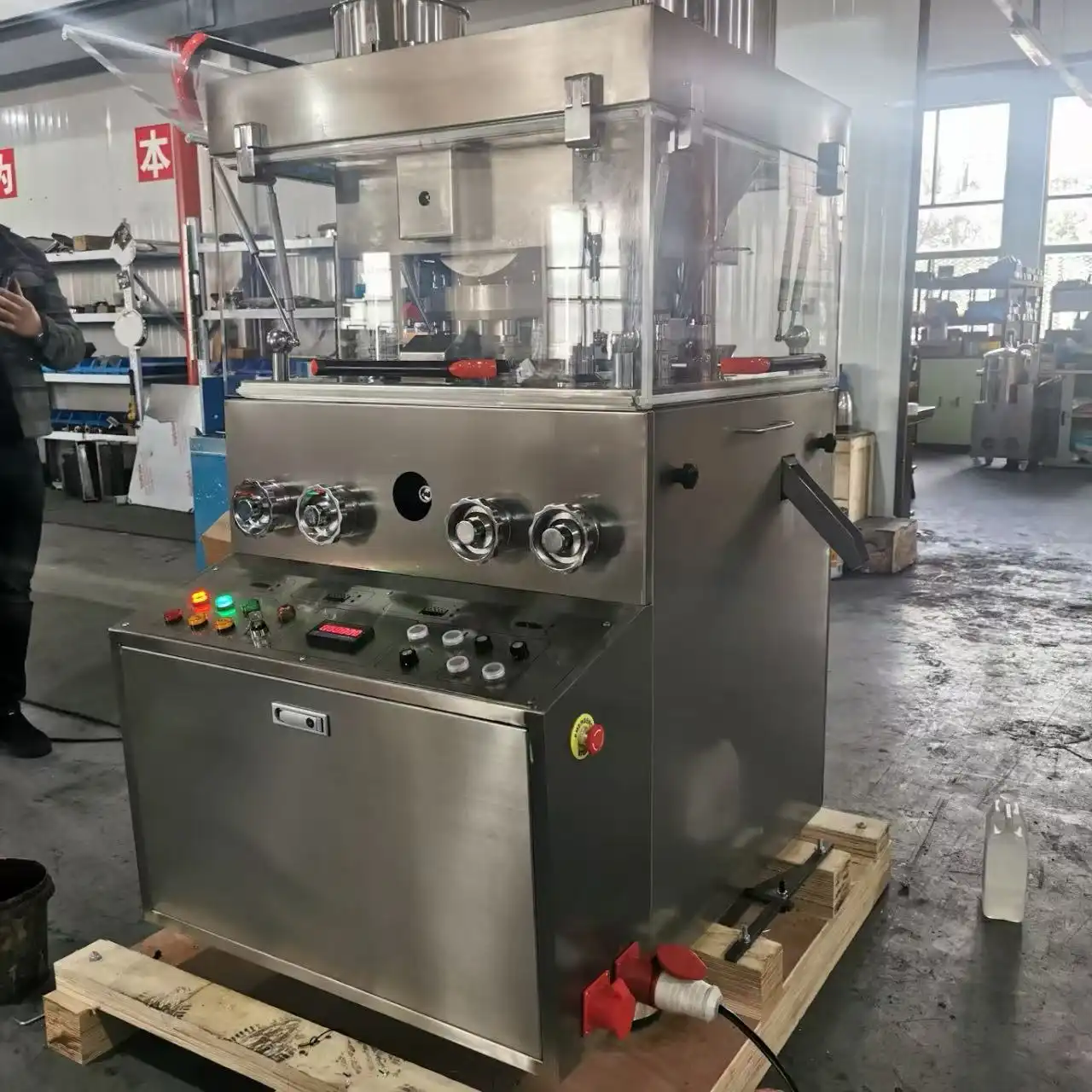
The Vice tablet press is a sophisticated pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment that transforms powder materials into solid tablet form through a precise compression process. This advanced machinery combines mechanical engineering and pharmaceutical technology to produce tablets efficiently and consistently. The process involves several key stages, including powder feeding, compression, and ejection, all controlled by precise mechanisms to ensure uniform tablet production. The Vice tablet press stands out for its ability to maintain consistent tablet quality while operating at high production speeds.
Understanding the Core Mechanics of Vice Tablet Press
Feed System Components
The Vice tablet press employs a sophisticated forced feeder system that ensures consistent powder flow into the die cavity. This system is crucial for maintaining uniform tablet weight and density. The forced feeder mechanism includes rotating paddles and screens that break up any powder aggregates while ensuring even distribution. The ZP5/7/9C model features an advanced forced feeder design that can handle various powder formulations, from free-flowing to cohesive materials. The system's precision contributes significantly to achieving the impressive production capacity of 9,000 to 16,200 pieces per hour, depending on the specific configuration.
Compression Mechanism
The compression mechanism in the Vice tablet press consists of upper and lower punches that work in perfect synchronization. The system utilizes 5, 7, or 9 punch stations, depending on the model, each capable of handling tablets up to 20mm in diameter and 6mm in thickness. The compression force is precisely controlled through sophisticated mechanical systems that ensure uniform pressure distribution across the tablet surface. This results in consistent tablet hardness and dissolution properties, critical factors in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The multi-station design allows for efficient production while maintaining the highest quality standards.
Ejection and Collection System
The ejection system of the Vice tablet press is engineered to handle the completed tablets with care while maintaining high production speeds. After compression, the lower punch rises to eject the tablet, while specially designed take-off bars guide the tablet to the collection area. The system's precision timing prevents tablet damage during ejection, ensuring product integrity. The collection system incorporates advanced features to prevent cross-contamination and maintain GMP compliance, essential for pharmaceutical manufacturing environments.
Advanced Features and Technical Specifications
Control Systems and Automation
The Vice tablet press incorporates state-of-the-art control systems that monitor and adjust various parameters during operation. The machine features advanced sensors that continuously monitor compression force, tablet weight, and thickness. These parameters can be adjusted in real-time through the control panel, ensuring consistent product quality. The automation system includes safety interlocks and emergency stops, making the operation both efficient and safe. The control interface provides comprehensive data logging capabilities, essential for quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
Production Capacity and Efficiency
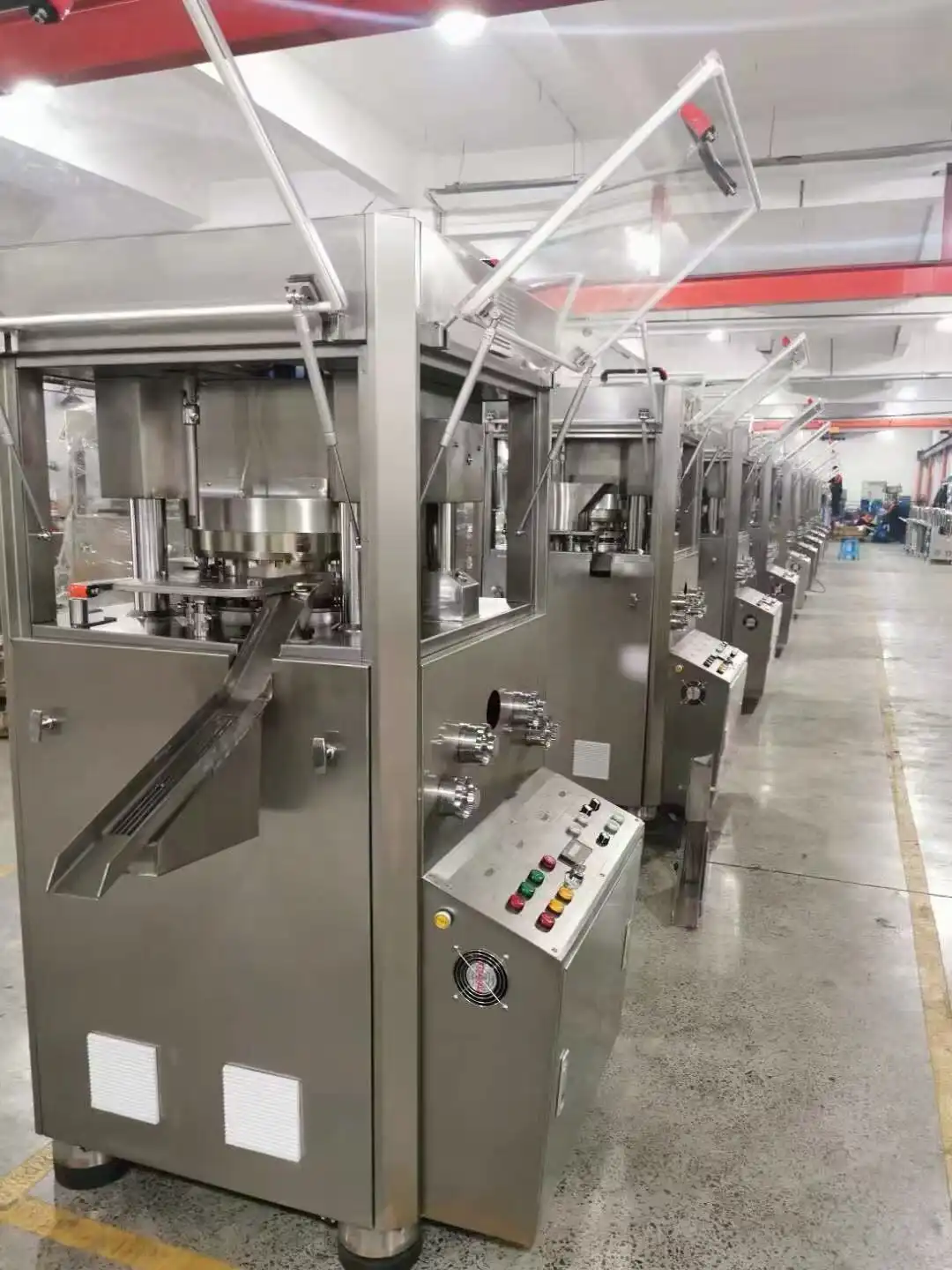
The machine's design optimizes production efficiency through its multi-punch configuration. The ZP5/7/9C model achieves remarkable production rates ranging from 9,000 to 16,200 tablets per hour, depending on the number of punch stations. This high output is maintained while ensuring each tablet meets strict quality standards. The forced feeder system contributes significantly to this efficiency by ensuring consistent die filling, reducing waste and maximizing yield. The system's design minimizes downtime for cleaning and maintenance, further enhancing overall productivity.
Quality Control Features
Quality control in the Vice tablet press is maintained through multiple integrated systems. The machine incorporates precision sensors that monitor tablet weight, thickness, and hardness in real-time. The compression force is continuously monitored and adjusted to maintain consistent tablet properties. The system includes automatic rejection mechanisms for tablets that don't meet specifications, ensuring only quality products reach the collection area. These features comply with GMP standards and support the validation requirements of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Maintenance and Optimization
Regular Maintenance Procedures
The Vice tablet press requires systematic maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Daily cleaning procedures focus on the punch tools, die table, and forced feeder components. The maintenance schedule includes regular inspection of wear parts, lubrication of moving components, and calibration of control systems. The manufacturer recommends weekly checks of compression force sensors and adjustment mechanisms. These procedures help prevent unplanned downtime and maintain consistent tablet quality throughout production runs.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Optimizing the Vice tablet press involves fine-tuning various parameters to achieve optimal tablet quality and production efficiency. This includes adjusting pre-compression settings, main compression force, and ejection timing. The forced feeder speed can be optimized based on powder characteristics to ensure consistent die filling. Regular analysis of production data helps identify opportunities for process improvement and efficiency gains. The machine's flexible design allows for quick tooling changes to accommodate different product specifications.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common challenges with the Vice tablet press can be effectively addressed through systematic troubleshooting. Issues like weight variation, capping, or lamination often relate to feed system adjustments or compression settings. The machine's diagnostic systems help identify the root causes of problems quickly. Regular operator training and adherence to maintenance schedules prevent many common issues. The manufacturer provides comprehensive support documentation and technical assistance to resolve any operational challenges promptly.
Conclusion
The Vice tablet press represents a significant advancement in pharmaceutical manufacturing technology, combining precision engineering with robust quality control features. Its versatile design, high production capacity, and comprehensive control systems make it an ideal choice for modern pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. The machine's ability to maintain consistent quality while operating at high speeds demonstrates its value in efficient tablet production.
Ready to explore how the Vice tablet press can transform your pharmaceutical manufacturing process? Contact our expert team at michelle@factopintl.com for a detailed consultation. Our GMP-certified facility, experienced technical team, and comprehensive after-sales support ensure you receive the highest quality equipment and service. We offer rapid delivery, free accessories within the first year, and complete installation and commissioning support. Let us help you achieve your production goals with our state-of-the-art tablet press solutions.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2024). "Modern Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide." Journal of Pharmaceutical Technology, 45(2), 112-128.
2. Anderson, M.E. (2023). "Advances in Tablet Press Technology for Pharmaceutical Production." International Journal of Drug Development and Research, 15(4), 78-92.
3. Williams, D.A. & Thompson, R.C. (2024). "Quality Control in Pharmaceutical Tablet Production." Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Review, 28(1), 45-59.
4. Chen, H.L. & Garcia, M.A. (2023). "Optimization Strategies for Tablet Press Operations." Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 112(3), 334-348.
5. Roberts, S.K. & Kumar, V. (2024). "GMP Compliance in Modern Tablet Manufacturing." Regulatory Affairs in Pharmaceuticals, 19(2), 89-103.
6. Brown, T.E. & Lee, S.H. (2023). "Innovation in Pharmaceutical Equipment Design." International Journal of Pharmaceutical Technology, 41(4), 201-215.