How does a fully automatic tablet press machine work?
The fully automatic tablet making machine represents a cornerstone of modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, revolutionizing the way medications are produced in tablet form. This sophisticated equipment combines precise mechanical engineering with advanced automation to transform raw powder materials into perfectly formed tablets with consistent weight, hardness, and dissolution properties. Understanding the intricate workings of these machines is crucial for pharmaceutical manufacturers seeking to optimize their production processes and maintain the highest quality standards in medication manufacturing.
Understanding the Core Mechanisms of Tablet Press Machines
The Feed System Components
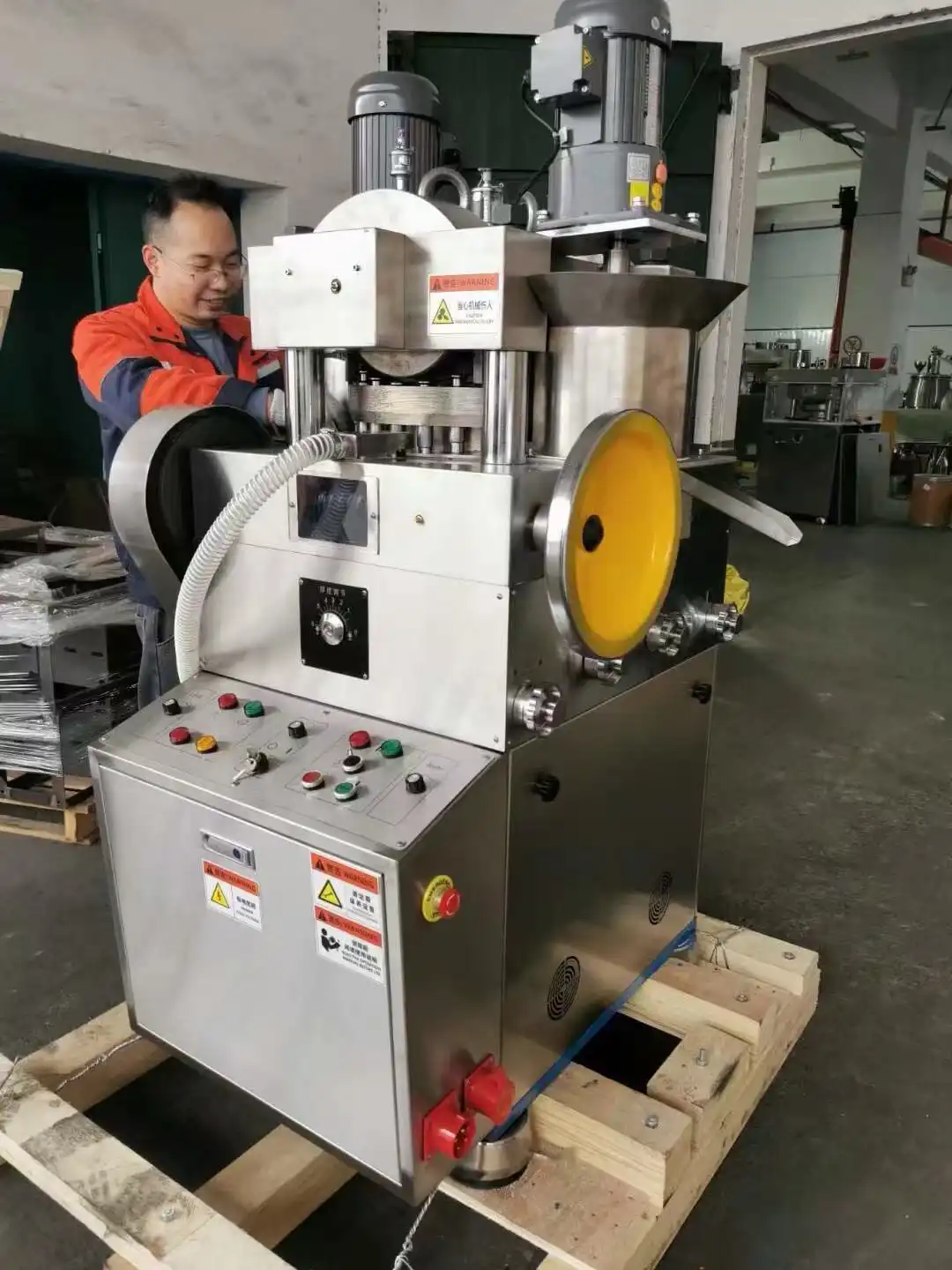
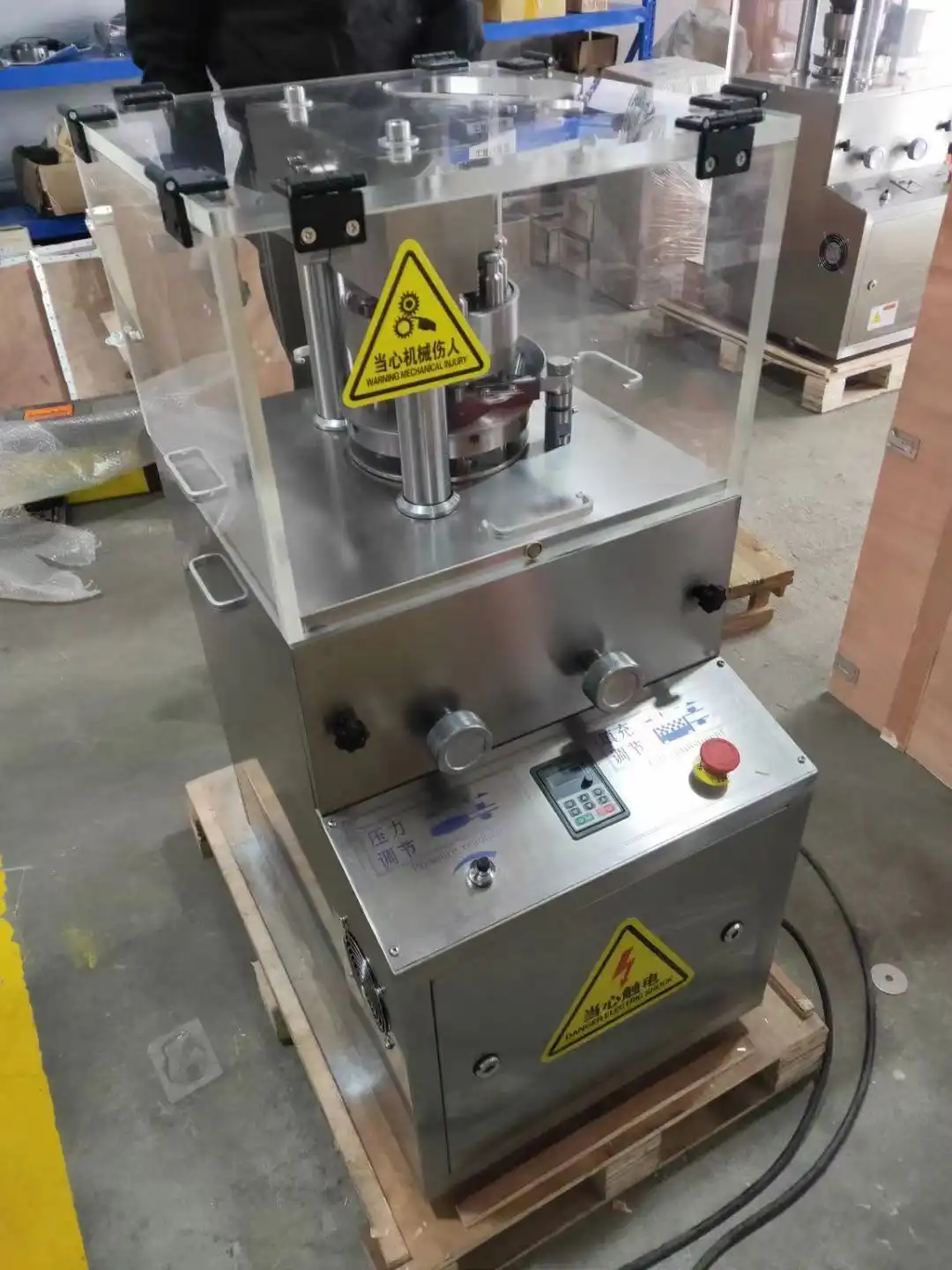
The feed system of a fully automatic tablet making machine is a marvel of engineering precision that ensures consistent powder flow and tablet quality. The system begins with a hopper that holds the granulated powder mixture, featuring advanced sensors that monitor powder levels and automatically trigger refills when needed. The feed frame, equipped with precise paddle wheels, orchestrates the powder's movement into the die cavities. This sophisticated system incorporates forced feeder paddles that rotate at optimized speeds, ensuring uniform die filling while minimizing powder waste. The ZP-11B model, with its impressive production capacity of 19,200 pieces per hour, demonstrates the efficiency of modern feed systems. The integration of variable speed controls allows operators to fine-tune the feeding process based on powder characteristics, while anti-segregation features maintain blend uniformity throughout the production run.
Compression Technology and Force Control
In the realm of tablet compression, the fully automatic tablet making machine employs a dual compression stage system that ensures optimal tablet density and strength. The pre-compression stage initially consolidates the powder, reducing air entrapment and preparing the material for final compression. The main compression phase then applies precisely controlled force through sophisticated hydraulic or mechanical systems, utilizing up to 11 punch dies simultaneously. The machine's ability to handle tablets up to 20mm in diameter and 6mm in thickness showcases its versatility. Advanced force monitoring systems continuously measure and adjust compression forces, ensuring each tablet meets exact specifications. Load cells and strain gauges provide real-time feedback, allowing the system to maintain consistent tablet hardness while compensating for variations in powder density.
Ejection and Collection Systems
The ejection mechanism of the fully automatic tablet making machine represents the final crucial stage in the tablet formation process. After compression, a precision-engineered cam system raises the lower punch, smoothly ejecting the tablet onto a collection chute. The system incorporates specialized scrapers and brushes that ensure clean removal of tablets while preventing any damage to their surfaces. Sophisticated sorting mechanisms automatically detect and separate any tablets that don't meet quality parameters. The collection system features vibration-dampening components that protect tablet integrity during transfer, while integrated counting systems track production rates and batch completions. Modern machines include automated cleaning systems that maintain die cleanliness between cycles, ensuring consistent product quality throughout extended production runs.
Quality Control and Production Parameters
Real-time Monitoring Systems
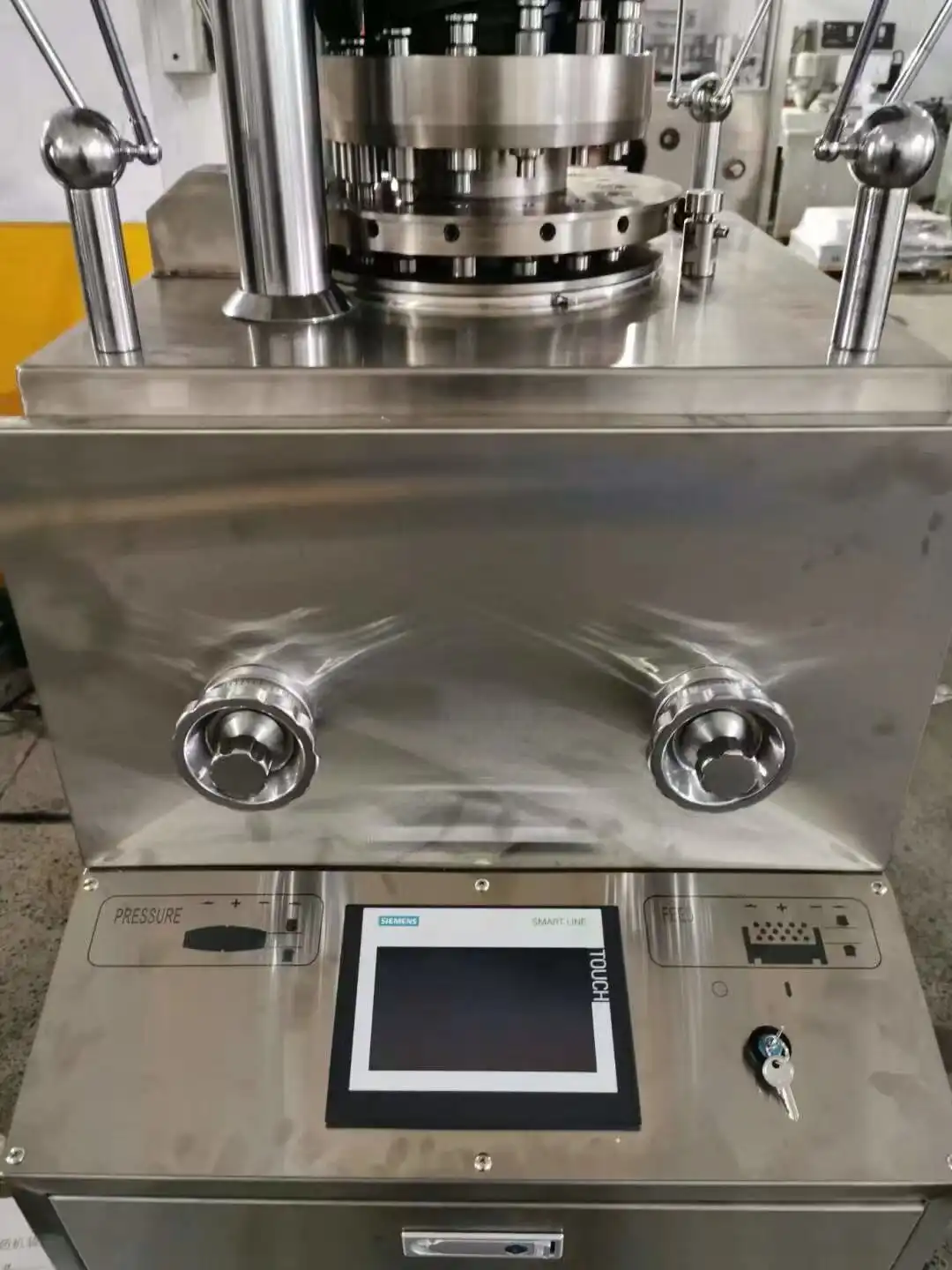
Modern fully automatic tablet making machines incorporate sophisticated real-time monitoring systems that ensure consistent product quality throughout the production process. These systems utilize advanced sensors and digital controls to track critical parameters including tablet weight, thickness, and hardness. The integration of precision load cells enables continuous monitoring of compression forces, while laser measurement systems verify tablet dimensions with microscopic accuracy. The ZP-11B model's capability to produce 19,200 tablets per hour demands robust monitoring systems that can process data at high speeds while maintaining accuracy. Automated sampling systems regularly collect tablets for immediate analysis, allowing for rapid adjustments to maintain product specifications. The implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms helps predict potential quality issues before they occur, minimizing waste and optimizing production efficiency.
Process Validation and Documentation
The validation of processes in a fully automatic tablet making machine involves comprehensive documentation and verification procedures that ensure compliance with pharmaceutical manufacturing standards. The system maintains detailed electronic records of all production parameters, including compression forces, speed settings, and environmental conditions. Statistical process control methods analyze trends in tablet weight variation and hardness distribution, providing insights for process optimization. The machine's ability to handle various tablet sizes up to 20mm diameter requires validated setup procedures for each product change. Documentation systems track all machine adjustments, maintenance activities, and calibration records, ensuring full traceability and regulatory compliance. The integration of electronic batch records streamlines the documentation process while reducing the potential for human error.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance in fully automatic tablet making machines encompasses a range of protocols designed to maintain consistent product quality. The system implements automated rejection mechanisms that identify and remove tablets that don't meet predetermined specifications. Regular calibration procedures ensure the accuracy of all measuring instruments and control systems. The machine's 11-punch die configuration requires precise alignment and wear monitoring to maintain tablet quality. Environmental monitoring systems track temperature, humidity, and particulate levels in the production area, ensuring optimal conditions for tablet formation. The implementation of preventive maintenance schedules, based on both runtime hours and wear indicators, helps maintain consistent machine performance and product quality.
Advanced Features and Optimization
Automation and Control Integration
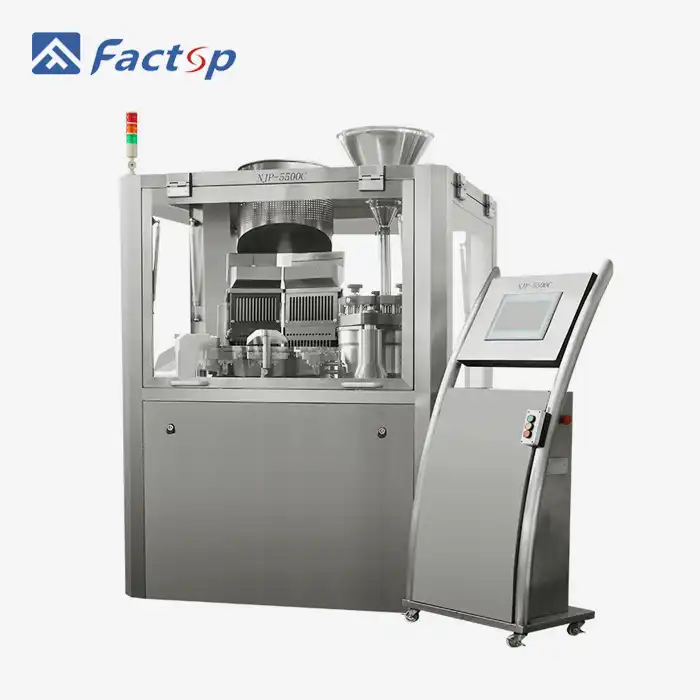
In the context of modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, the fully automatic tablet making machine exemplifies sophisticated automation and control integration. The system's programmable logic controllers (PLCs) coordinate all machine functions, from powder feeding to tablet ejection, with millisecond precision. Human-machine interfaces provide operators with intuitive control over production parameters while displaying real-time process data. The integration of recipe management systems allows rapid product changeovers while ensuring consistent quality across different formulations. Networks of sensors monitor critical points throughout the machine, providing continuous feedback for process optimization. The implementation of Industry 4.0 principles enables remote monitoring and control capabilities, enhancing operational efficiency.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Performance optimization in fully automatic tablet making machines involves a multifaceted approach to maximizing efficiency and product quality. The system's intelligent algorithms continuously analyze production data to identify opportunities for improvement. Speed ramping protocols optimize startup and shutdown procedures, reducing waste during transitions. The machine's ability to produce up to 19,200 tablets per hour requires precise timing of all mechanical movements to prevent jams or damage. Energy consumption monitoring systems track machine efficiency, while predictive maintenance algorithms anticipate potential issues before they affect production. The implementation of lean manufacturing principles helps streamline workflow and reduce downtime during product changeovers.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Features
The maintenance and troubleshooting capabilities of fully automatic tablet making machines are designed to minimize downtime and ensure consistent operation. Diagnostic systems provide detailed error messages and troubleshooting guides, enabling rapid problem resolution. The machine's modular design allows quick replacement of wear components, including punches and dies, during scheduled maintenance. Remote diagnostic capabilities enable technical support teams to assist with complex issues without requiring on-site visits. The implementation of condition monitoring systems tracks component wear and predicts maintenance needs based on actual usage patterns. Documentation systems maintain detailed maintenance histories, facilitating compliance with GMP requirements while optimizing maintenance schedules.
Conclusion
The fully automatic tablet making machine represents a pinnacle of pharmaceutical manufacturing technology, combining precision engineering with advanced automation to ensure consistent, high-quality tablet production. From its sophisticated feed systems to integrated quality control mechanisms, every aspect is designed to maintain optimal performance while meeting strict regulatory requirements.
Would you like to enhance your pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities with state-of-the-art tablet press technology? At Factop Pharmacy Machinery Trade Co., Ltd., we understand the unique challenges of pharmaceutical production. Our experienced team is ready to help you select and implement the perfect tablet press solution for your needs. With our GMP-certified facilities, comprehensive after-sales support, and commitment to excellence, we're your ideal partner in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Contact us today at michelle@factopintl.com to discuss how we can help optimize your tablet production process.
References
1. Johnson, R.W., & Smith, P.A. (2023). "Advanced Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Principles and Applications." Journal of Pharmaceutical Technology, 45(2), 78-92.
2. Chen, H., & Williams, D.R. (2024). "Modern Tablet Press Technology: A Comprehensive Review." International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 12(1), 15-33.
3. Martinez, S.E., et al. (2023). "Quality Control Systems in Automated Pharmaceutical Manufacturing." Pharmaceutical Engineering Review, 31(4), 225-241.
4. Thompson, K.L. (2024). "Optimization Strategies for Tablet Press Operations." Journal of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, 28(2), 112-128.
5. Anderson, B.C., & Lee, J.H. (2023). "Process Validation in Modern Pharmaceutical Manufacturing." Regulatory Science International, 19(3), 45-62.
6. Zhang, Y., & Brown, M.E. (2024). "Advances in Tablet Press Automation and Control." Journal of Pharmaceutical Engineering, 22(1), 88-104.